Smart Grids Austria
Mission Statement
The Technology Platform Smart Grids Austria is an association of relevant stakeholders in the field of electrical power supply. The Platform was founded in 2008 with the support of the Climate and Energy Fund, the Ministry of Transport, Innovation and Technology and the Ministry of Economy and since then the FEEI - association of electrical and electronic industries and Oesterreichs Energie support as host organizations.
The aim of the Platform is to pool joint forces for future intelligent electricity grids in order to support an energy- and cost- efficient system operation.
Synergies through coordination of stakeholders from industry, energy sector, research and public bodies should be used efficiently.
Austrian expertise in smart grids should be strengthened by flagship projects and made visible internationally.
Technology Platform Smart Grids Austria: The Goals
Information on current and strategic smart grids projects
The Technology Platform provides a running range of information or working on current and strategic smart grids questions.
Shaping the Framework
The Technology Platform creates with its membership structure a framework for co-ordination of Austrian Stakeholders and thus enables a uniform Austrian perspective on the subject of smart grids. The Platform can help shape decisively with its experts the general conditions for the conversion of the energy system.
International Network
The Technology Platform is in exchange with international Platforms and initiatives, thus enabling the active contribution of Austrian interests in international cooperation and mutual exchange of information.
Technology Platform Smart Grids Austria: The Tasks
The cross-sectoral Coordination Forum
Network and Coordination:
- bundling of forces and benefits of synergies through continuous networking and coordination of the sectors
- integration of not yet addressed stakeholders and international experiences
- setting a common focus, coordinate objectives to ensure a structured approach and implementation
- find new project partners in network more easily
Information and Solution:
- access to broad cross sectoral expertise
- prepare and communicate Information and coordinated positions for decision makers
- demonstrate national and international experience solutions in network, that barriers can be overcome
Innovation- und Initiative:
- contribute to new themes, technologies, system approaches etc. into the discussion
- active participation and improve conditions by pulses to research and Technology policy, education and the legal framework
Design and Positioning:
- promote demonstration projects effectively, by combining the findings and experience of all partners.
- position Austria as a leading market through flagship Projects
Team
Technology Platform Smart Grids Austria:
Managing Director
Christoph Wanzenböck, MA, MBA
E: christoph.wanzenboeck@smartgrids.at
Projects
IES – Integrating the Energy System Austria
Please refer to our English project page: IES - Integrating the Energy System (eng.)

The Technology Roadmap Smart Grids Austria
In the years 2014/15 the Technology Roadmap Smart Grids Austria was developed by the Austrian Smart Grids experts with a time horizon till 2020. This is a complete overview of the actual state of development and further concrete steps for implementation and provides the benefits for industry, energy and for the society, as well as aspects in the training and awareness in the population.
The milestones for the implementation concerning the further development of technology, regulatory and legislative measures, large-scale system validation and implementation phase.
In the Technology Roadmap three key steps in implementation of smart grids were identified for the coming years.
- The first step is an ICT total architecture, starting from the actual state of the ICT architecture to develop. The path to a unified, scalable and efficient solution makes a clarification and optimization of process issues through a large-scale system validation necessary.
- The second step is that large-scale validation projects are necessary. Whole distribution network areas with the appropriate technology should be equipped throughout for the validation and field testing of systems approaches in large-scale implementation projects.
- The third step of the development of a lead market as an internationally visible reference for Austria is important to allow the positioning of Austrian companies as technology leaders.
For the implementation of the key steps of the Technology Roadmap an action for the relevant actors has been identified. These actors are the representatives of the energy industry such as network operators and electricity suppliers, technology providers and public authorities.
The Austrian industry, energy and research departments have expectations that by implementing the national Technology Roadmap into international technology leadership will strengthen the business location Austria.
Contact
Angela Berger
Managing Director
Technology Platform Smart Grids Austria
E: angela.berger@smartgrids.at
Dowloads
Technology Roadmap Management Summary
Technology Roadmap Document
Smart Grids Model Regions in Austria
Central steps for implementation of Smart Grids in Austria
RASSA–Initiative
Starting Position
Motivated by the need to efficiently integrate volatile energy sources, innovative smart grid technologies have been recently developed. This has led to a significant increase in the use of ICT technologies within the electrical power supply system. This situation introduces two major challenges: the need for seamless interoperability, in order to ensure components function correctly as part of an overall complex system; and the importance of safety, security and privacy measures to protect the system from cyber-attacks and enhance end-user acceptance. Both of these issues need to be addressed early during the design phase of the smart grid, in order to ensure the sustainability and security of future energy supply.
Previous projects and pilot deployments in Europe and Austria have gone some of the way to address these challenges, but only provide partial solutions. In order to tackle the challenges of interoperability and security essential for the next five to ten years a national smart grid reference architecture for Austria is imperative. A holistic solution that offers security-by-design reduces the attack surface and thus the risk from cyber-attacks targeted, for example, at critical control elements. In this way, the availability of power supply can be ensured, which strengthens the competitive position of Austria as a business location and its leading role in the European smart grid market.
Goal of the RASSA-Initiative
The RASSA Initiative's goals can be listed as:
- Definition of a homogeneous reference architecture for Smart Grids in Austria, throughout considering aspects like security, safety, resilience, privacy
- Reaching a consensus among all relevant stakeholders on contents and utilization of a reference architecture
- Degrees of freedom allow competitive realizations of RASSA
- Providing concrete guidance for migration of today’s system to a future smart grid infrastructure in terms of the reference architecture
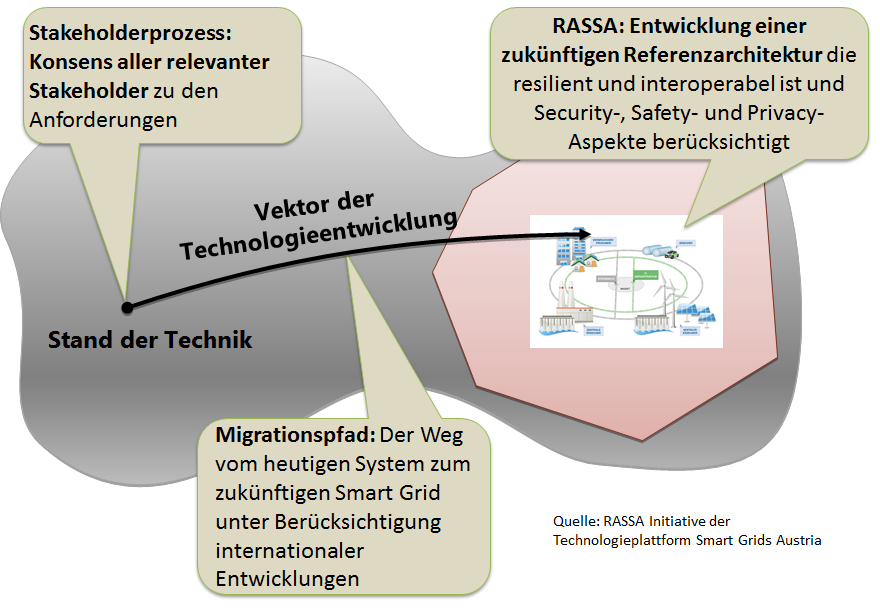
A reference architecture offers vendor-neutral, technical specifications to the minimum requirements and interfaces modular "building blocks" for specific system solutions. The reference architecture is based on selected use cases, actors and their relationships and the time specified processes, data exchanges, safety and standard requirements and components.
Modeling of Smart Grid Systems
The development of smart grid system architectures represents a complex challenge, involving the different stakeholders from different domains. To enable stakeholder involvement and interdisciplinary development a common language or a common reference system is required.
In the Framework of the M / 490 mandate with the Smart Grid Architecture Model (SGAM) was presented, which is now widely accepted as a reference system. In order to enable practical application of this reference system, the FH Salzburg (Security and Control Josef Ressel Center for User-Centric Smart Grid Privacy) has developed the SGAM-Toolbox. This toolbox provides a domain- specific modeling language that enables modeling of smart grid systems in the context of the SGAM.
Starting points for the reference architecture:
There are already several reference architectures that have been created taking into account extensive use case collections. A context of existing international and national work on which is based the development of the Austrian reference architecture.
Benefits of RASSA Reference Architecture
- RASSA prepares the next steps in the transformation of power grids in advance. The current system architecture will no longer correspond the future smart grid architecture. The reference architecture addresses the functional sequence of future use cases in a prioritized timeline.
- The reference architecture ensures a common consideration of the energy and ICT system. A coordinated overall solution has a lower contact surface, so that targeted attacks can be prevented. Therefore the risk of power failures due to cyber-attacks is reduced.
- A reference architecture provides modular "building blocks" for specific system solutions. Simultaneously, the reference architecture leaves enough freedom for individual design. Thus secure, interoperable Smart Grid applications can be implemented in a simple and consistent manner.
